DSLR Basics: Day 1
Preparation
- Reserve SL1/SL2 camera(s) for you and any students who need.
- Reserve the studio for class time during Day 2 (reserve two 30 minute slots so you don’t have to check in and no one can reserve the studio while you’re in there)
- Email students the week before class, reminding them to bring their DSLR’s, or check one out from the equipment room (provide instructions and link to online reservation). They can also choose to use a camera we will provide during the class. For the purpose of this class, cameras can be borrowed from the Experiential Zone Help Desk. They are not our usual SL1s or SL2s so you should get a feel for them when prepping for class, and make sure you know how to adjust settings! Cameras should be “checked out” at the beginning of class using the following form. And should be returned at the end of each class. They should not be taken home! It is your job to print this form and bring it to class, and make sure each camera is returned at the end of class.
Objectives
By the end of the class, students will be able to:
- Understand the tenets of exposure
- ISO
- Shutter Speed
- Aperture
- Become familiar with basic functionality of DSLR cameras
- Modes (P Tv Av M)
- Adjusting exposure
- Shooting in Manual and shooting in RAW
- Basics of composition
- Rule of thirds
- How to adjust focus (manually and automatically)
Introduction
This is the link to the Google Slides presentation.
Create/practice your lesson plan WITH the slideshow. It is basically your lesson plan, but it doesn’t have much text so you still have to know your stuff!
Photography literally means “drawing with light.” So let’s talk about how light turns into a picture.
A digital single-lens reflex camera (digital SLR or DSLR) is a digital camera that combines the SLR (single-lens reflex camera) with a digital imaging sensor as opposed to film. The reflex design scheme is the primary difference between a DSLR and other digital cameras. In the reflex design, light travels through the lens, then to a mirror that alternates to send the image to either the viewfinder or the image sensor. The traditional alternative would be to have a viewfinder with its own lens, hence the term “single lens” for this design. By using only one lens, the viewfinder of a DSLR presents an image that will not differ substantially from what is captured by the camera sensor.
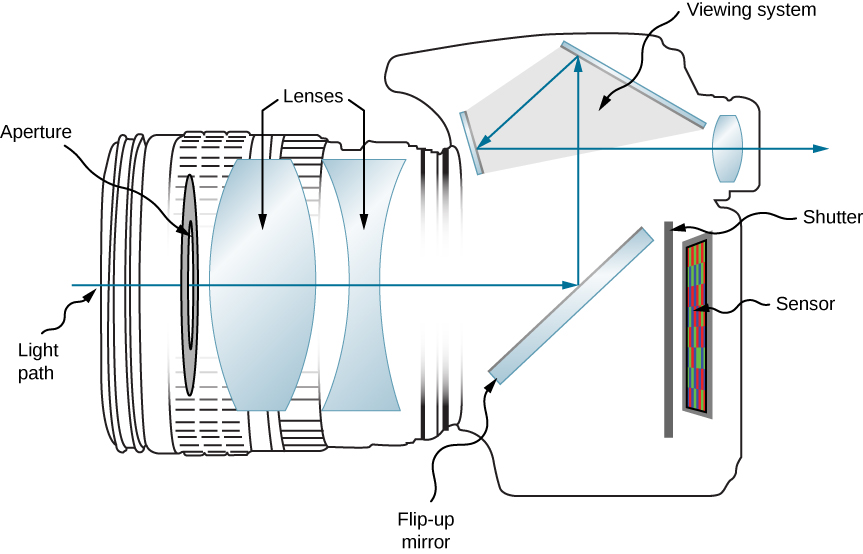

DSLRs largely replaced film-based SLRs during the 2000s, and despite the rising popularity of mirrorless system cameras 2010s, DSLRs remain the most common type of interchangeable lens camera in use today.
RAW Files

- Explain RAW and why they should use it
- Show examples of editing a JPEG vs. RAW (you’ll have to download these and open them in Ps or Lr and bring down exposure settings to show them how much better RAW is).
- Change image quality settings to shoot RAW
- (This will take more memory on your SD card)
- Your pictures will also initially look more flat and dull than the compressed JPEGS but it is worth it in post.
Exposure
- In photography, exposure is the amount of light which reaches your camera sensor or film. It is a crucial part of how bright or dark your pictures appear.
- Your exposure is determined by the light in the scene you are photographing and the look you are going for (high-key vs. low-key)
- You control your exposure with 3 things:

- In order to control your exposure completely, first you have to set your camera to Manual mode. (Have everyone do this–you’ll explain the other modes later).
- ISO is the sensitivity of your digital image sensor. The higher it is, the more sensitive to light.
- However, higher ISO also introduces noise into your image. It looks grainy which is not usually preferred.

- Show students how to change their ISO, and have them take a couple pictures with low/high ISO.
- Shutter Speed determines how long your lens stays open. It is measured by seconds (fractions of a second) and the longer you leave it open, the more light enters (and more motion blur you potentially get).
- Show students how to change their shutter speed and give them a couple minutes to take pictures with fast/slow shutter speeds.
- Aperture is how wide your lens opening is. This can be the most confusing of the 3 tenets of exposure…because the lower your f-number (Aperture f/1.4 for example), the wider your aperture, and the more shallow your depth of field.
- Depth of field is how narrow your plane of focus is. The more shallow your DOF, the shorter your plane of focus, giving you a blurry background.
- Generally, you want to use a large aperture for portraits, small aperture (longer DOF) for landscapes, architecture
- Three things that affect DOF are: aperture, distance from subject, focal length
- Show students how to change their aperture and give them a couple minutes to take pictures with small/large apertures.
- The tenets of exposure can be confusing. Pass out cheat sheets.
- Teach them how to “read” a lens (focal length and lowest aperture setting)
- You may even mention prime/fixed lenses.
How to tell if you have a good exposure:
- Take test shots
- Check your light meter
Modes
- Nikon=M A S P / Canon=M Av Tv P
- M=Manual
- A / Av = Aperture priority / Aperture value
which means your shutter speed will be automatically adjusted to compensate for whatever aperture you select - S / Tv = Shutter priority / Time value
which means your aperture will be automatically adjusted to compensate for whatever shutter speed you pick - P=Program
Automatic, except you can change shutter speed and aperture if you want - Never shoot Auto
Focusing
- Manual vs. Auto-focus
- Half-press the shutter to focus, full press to take picture
- Hold AE-lock and half-press the shutter to lock your focus and then move composition and press the shutter fully to take the picture
- This also determines your metering (which determines your exposure or in Manual mode, just gives you a read of the exposure)
- Teach the basics of composition (rule of thirds)
If there’s time, have them take this quiz during class: tiny.cc/DSLRquiz
